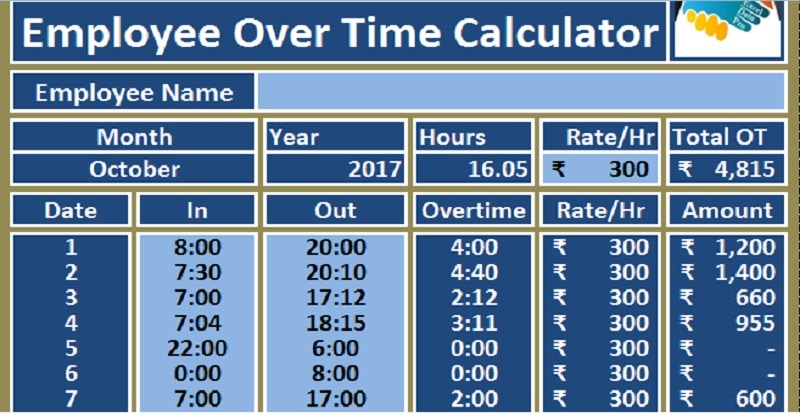
Overtime pay is an important aspect of fair compensation, ensuring employees are rewarded for working beyond standard hours. However, calculating it correctly can be challenging, especially when dealing with different employment types, varying laws, and specific contractual agreements. Mistakes in overtime calculations can lead to compliance issues, employee dissatisfaction, and costly disputes.
This guide explains how to calculate overtime pay accurately for both hourly and salaried workers, while highlighting key considerations to ensure compliance.
Understanding Overtime Basics
Overtime pay is additional compensation given to employees who work beyond a certain threshold of hours, often defined by labour laws or employment contracts.
1. Standard Work Hours:
Many countries define a standard workweek (e.g., 40 hours in the United States, 38 hours in Australia, 35 hours in France).
2. Overtime Rate:
Commonly 1.5 times the regular hourly rate, but this varies by jurisdiction and employment agreement.
3. Eligibility:
Not all employees are entitled to overtime; exemptions may apply to certain roles or industries.
Calculating Overtime for Hourly Workers
Hourly employees are generally the simplest group for overtime calculation because their pay is directly tied to the hours they work.
Step-by-Step Calculation of overtime for hourly workers:
1. Determine the Standard Rate
Identify the employee’s regular hourly wage.
2. Identify Overtime Hours
Calculate the hours worked beyond the standard threshold (e.g., over 40 hours in a week).
3. Apply the Overtime Multiplier
Multiply overtime hours by 1.5 (or the rate specified by law/contract).
4. Add Regular and Overtime Pay
Combine both amounts for total pay.
Calculating Overtime for Salaried Workers
Salaried employees can also be eligible for overtime if they are classified as “non-exempt” under labour laws. Calculating their overtime involves converting their salary into an hourly rate.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
1. Find the Weekly Salary
Divide the annual salary by the number of weeks in a year (52).
2. Determine the Hourly Rate
Divide the weekly salary by the standard workweek hours.
3. Identify Overtime Hours
Count hours worked beyond the standard threshold.
4. Apply Overtime Rate
Multiply the hourly rate by the overtime multiplier and the number of overtime hours.
Key Considerations
1. Legal Compliance
- Labour laws vary by country and sometimes by region or state.
- Always check local rules on thresholds, rates, and exemptions.
2. Contractual Terms
- Some employers offer higher-than-mandated overtime rates.
- Certain agreements may allow for “time off in lieu” instead of extra pay.
3. Different Multipliers
- Some regions have higher rates for weekends, public holidays, or night shifts.
- Double time may apply in certain cases, such as excessive overtime or specific industries.
4. Accurate Time Tracking
- Use reliable timekeeping systems to capture exact hours worked.
- Inaccurate records can lead to disputes and penalties.
Conclusion
Calculating overtime pay correctly is both a legal requirement and a way to maintain employee trust. For hourly workers, the process is straightforward, but salaried workers require extra steps to determine their regular rate.
Employers should familiarise themselves with local labour laws, maintain accurate records, and apply consistent calculations. By doing so, they can ensure fair compensation, avoid compliance issues, and foster a positive workplace culture.

